Prerequisite: You need to familiar with the box model
Understanding the differences between clientHeight/clientLeft, offsetHeight/offsetLeft, and scrollTop/scrollLeft in the context of the Document Object Model (DOM) is crucial for effective web design and development. These properties are used to measure different aspects of elements’ size and position in relation to their content, padding, border, and scroll position.
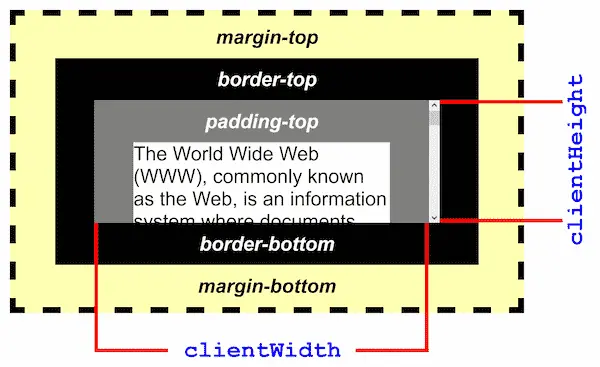
Client
clientHeightandclientLeftwill give you the height and width of an element including padding. However,clientwill not calculate the size of the borders and margins.clientHeight/clientLeftare useful for understanding the visible part of an element, particularly for styling purposes or when dealing with scrolling.- It’s a read-only property, which means you can not modify the params and generate action.
Offset
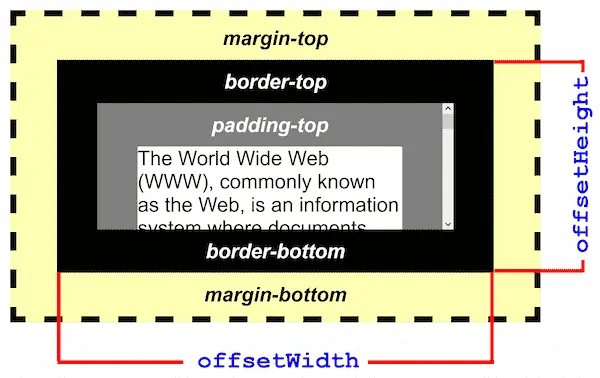
- Similar with
client,offsetHeight,offsetLeftwill output the element height and width but including verical and horizontal border, in pixel. - offsetHeight/offsetLeft are often used when you need to know the actual size of the element including borders and its position in the layout.
- Same as client,
offsetHeight/offsetLeftis a read only param.
Scroll
scrollTopproperty gets or sets the number of pixels that an element’s content is scrolled vertically.scrollLeftis similar but for the horizontal axis. UnlikescrollTop,scrollLeftseldom use in current mainstream web pages since most of pages are developed vertically.scrollTop/scrollLeftare crucial for controlling and accessing the scroll position within an element, especially in scenarios involving dynamic content loading or scroll-based animations.
Typically,
scrollTopis a good property to calculate the whole window scroll distance. This distance can be used as a condition for partial attribute changes. For example, we can determine the entry and exit of the header by judging the distance the customer has scroll down. Here is the code:
<script>
const header = document.querySelector('.header')
const module = document.querySelector('.module')
window.addEventListener('scroll',function (){
const topLength = document.documentElement.scrollTop
// if (topLength >= module.offsetTop){
// header.style.top = '0px'
// }
// else {
// header.style.top = '-50px'
// }
header.style.top = topLength>=module.offsetTop?'0px':'-50px'
})
</script>
- Besides,
scrollTopis a writable param, which mean you can use it as a jump fumction that quickly scroll to specific position. This will be very helpful when you want to creat an sidebar navigator.
Understanding these properties and their differences is key in web development, especially when dealing with dynamic layouts, responsive designs, and interactive content. Each property serves specific purposes and choosing the right one depends on the particular layout or behavior you want to achieve.