Continuous Integration
Continuous Integration (CI) is a software development practice where developers frequently merge their code changes into a central repository, preferably multiple times a day. Each merge triggers an automated build and testing process, which helps in identifying and addressing integration errors as quickly as possible. The primary purpose of CI is to improve software quality and accelerate the development process.
Key aspects of Continuous Integration include:
Automated Building and Testing: Automated tools are used to compile the code and run tests every time changes are integrated. This ensures that the software is always in a state where it can be deployed.
Version Control Integration: CI relies heavily on version control systems to manage changes to the codebase. Developers are encouraged to commit changes frequently, which supports the detection of conflicts and integration issues early in the development cycle.
Immediate Feedback: Developers receive immediate feedback on their commits. If a build or test fails, the system alerts the responsible developers so they can fix the issue promptly. This reduces the debugging time later in the development cycle.
Consistency: The use of automated tools ensures that builds and tests are executed in a consistent environment. This minimizes the “it works on my machine” syndrome, where code behaves differently on different developers’ environments.
Efficiency: Automated tests and builds reduce the manual work required from developers, allowing them to focus on writing code. This efficiency can lead to faster development cycles and quicker time to market.
The purpose of Continuous Integration is to:
Detect and address integration issues early: By integrating frequently, issues can be identified and resolved early in the development process, reducing the complexity of fixing bugs.
Improve software quality: Regular testing ensures that defects are caught and corrected early, improving the overall quality of the software.
Reduce time to market: Efficient processes and early detection of issues lead to shorter development cycles, enabling faster release of products.
Enhance project visibility and feedback: Continuous Integration provides a clear insight into the project’s health through the status of builds and tests, making it easier to assess progress.
Overall, Continuous Integration is a critical component of modern software development practices, particularly in agile environments. It supports the development of high-quality software while enabling teams to be more productive and responsive to changes.
Spring boot
Spring boot itself has its own continuous integration located in GitHub Actions. The specific configuration is written like this:
name: Build Pull Request
on: pull_request
permissions:
contents: read
jobs:
build:
name: Build pull request
runs-on: ubuntu22-8-32
if: ${{ github.repository == 'spring-projects/spring-boot' }}
steps:
- name: Set up JDK 17
uses: actions/setup-java@v4
with:
java-version: '17'
distribution: 'liberica'
- name: Check out code
uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Validate Gradle wrapper
uses: gradle/wrapper-validation-action@699bb18358f12c5b78b37bb0111d3a0e2276e0e2
- name: Set up Gradle
uses: gradle/gradle-build-action@3b1b3b9a2104c2b47fbae53f3938079c00c9bb87
- name: Build
env:
CI: 'true'
GRADLE_ENTERPRISE_URL: 'https://ge.spring.io'
run: ./gradlew -Dorg.gradle.internal.launcher.welcomeMessageEnabled=false --no-daemon --no-parallel --continue build
- name: Print JVM thread dumps when cancelled
uses: ./.github/actions/print-jvm-thread-dumps
if: cancelled()
- name: Upload build reports
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
if: failure()
with:
name: build-reports
path: '**/build/reports/'
However, if not make any changes, it will be automatically skip rather than triggered.

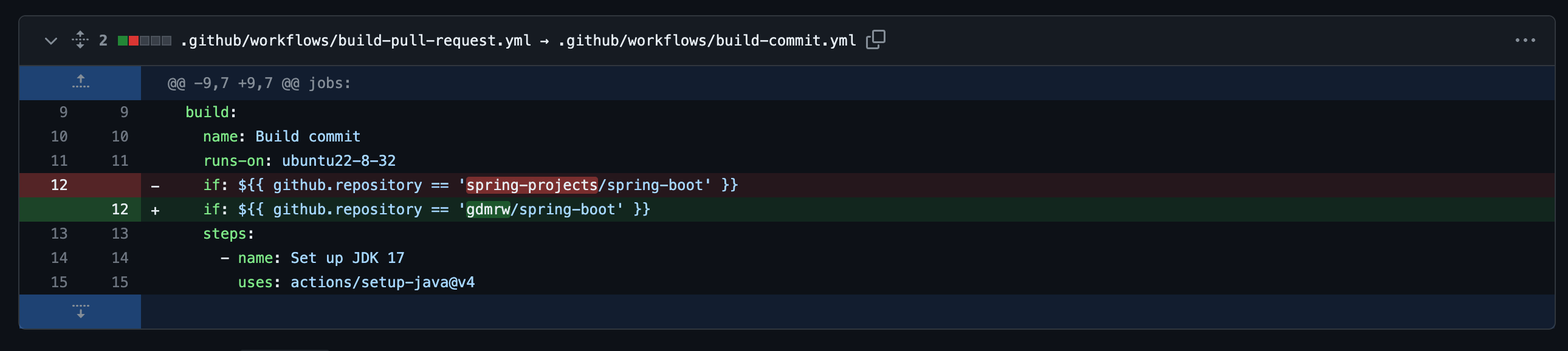
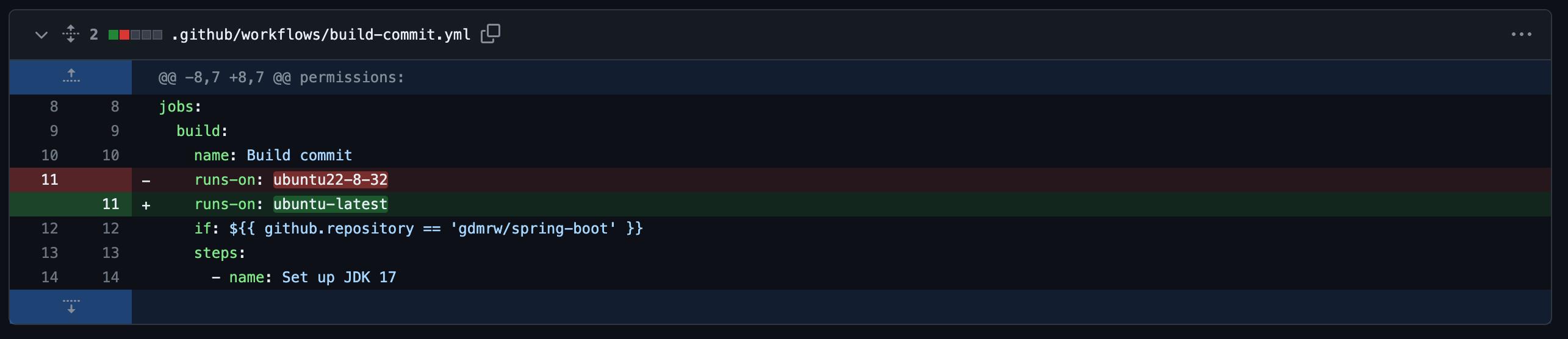
Three places modified to make sure the action builds trigger. The first one changes the trigger type, from pull request to commit. The second one changes the repo location. And the last one makes an adjustment on system type to make it match GitHub Action’s environment identifier.
Let’s make a push to see if github actions working properly.
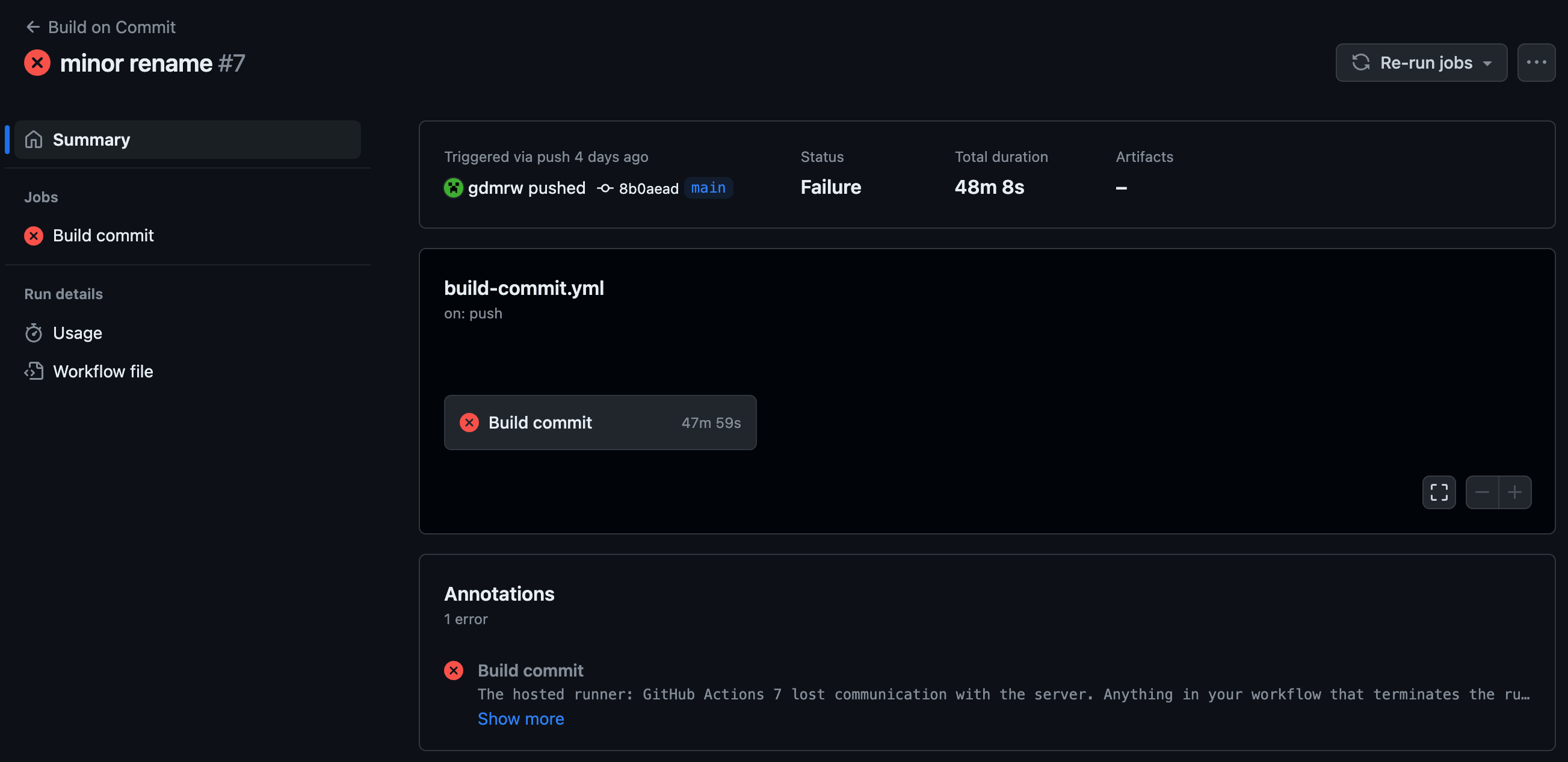
After 50 minutes wait, the build action gets successfully triggered, but the build failed. We get not log file except one annotation:
Build commit The hosted runner: GitHub Actions 7 lost communication with the server. Anything in your workflow that terminates the runner process, starves it for CPU/Memory, or blocks its network access can cause this error.
GitHub action unexpectedly lost the connection to the server.Based on its prompt, I speculate the system crashes due to out of memory . Spring boot is so huge that an average performance server is unable to handle this task. I checked peers build time. On average, it only takes 5 to 10 minutes to complete the build on one platform, maximum no over 15min.
Fortunately, We made a pull request in the previous coverage test, which gave us a chance to call the build system of the main repository, we can see what’s going on inside.
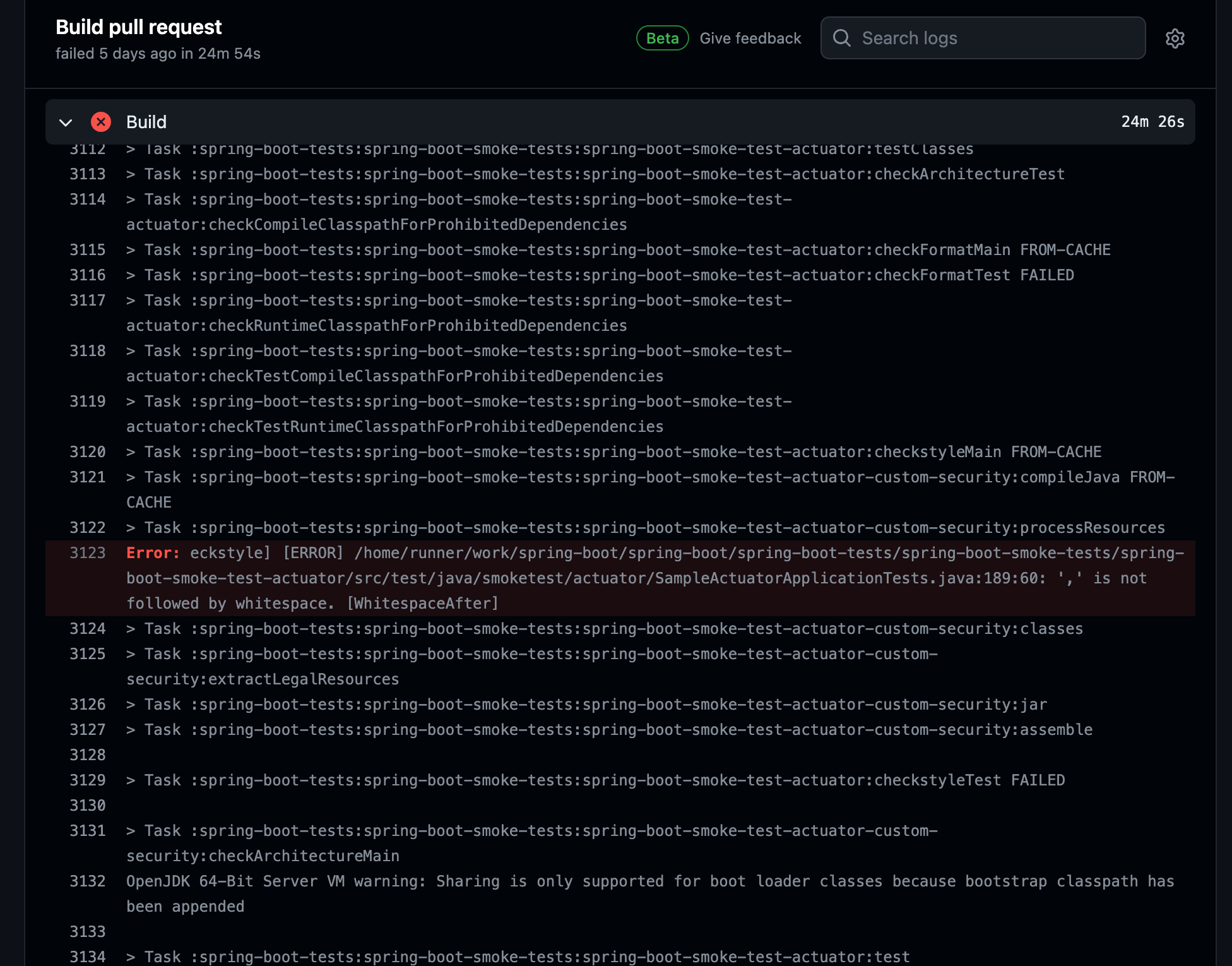
In the right conor of the panel, we can clearly see that even with a well-tuned server, it still took 24 minutes to complete the build.Furthermore, a total of five thousand lines were recorded in the log. In line 3123, we can notice that as a widely used framework, spring boot has strict content review standards. The red block is the cause of the build failure, which is caused by my introduced code. Springboot’s build configuration introduces format detection, which they call check-style, and uses this to normalize all code blocks. You will see that I just miss one space after a comma, a whole build failure. I adjusted this and committed to the remote repo again.
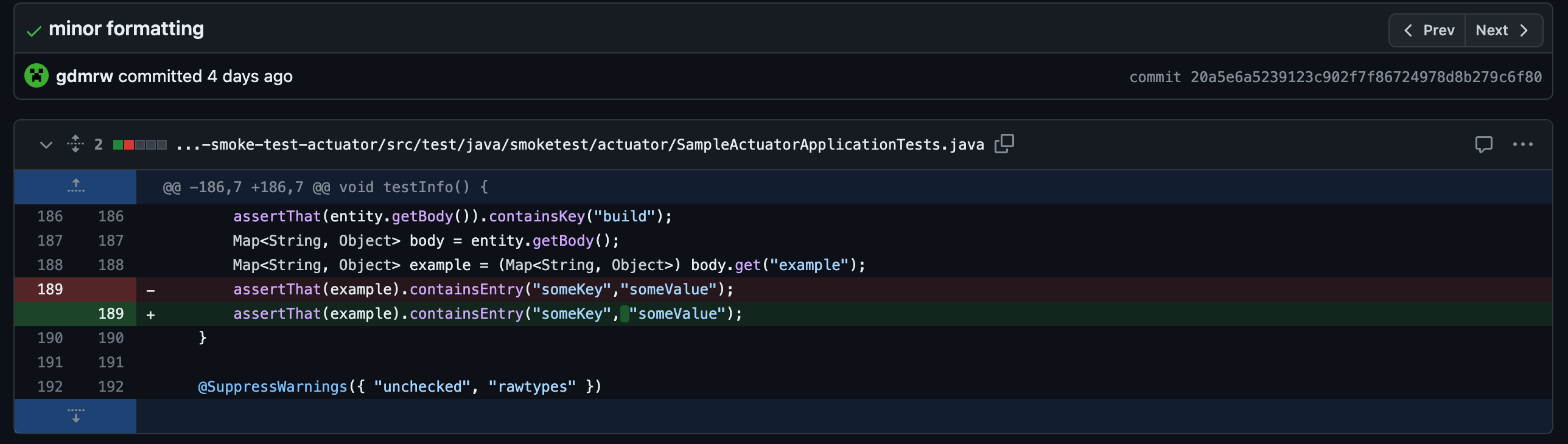
You can see that after the new commit new build finishes successfully.Below are excution details.
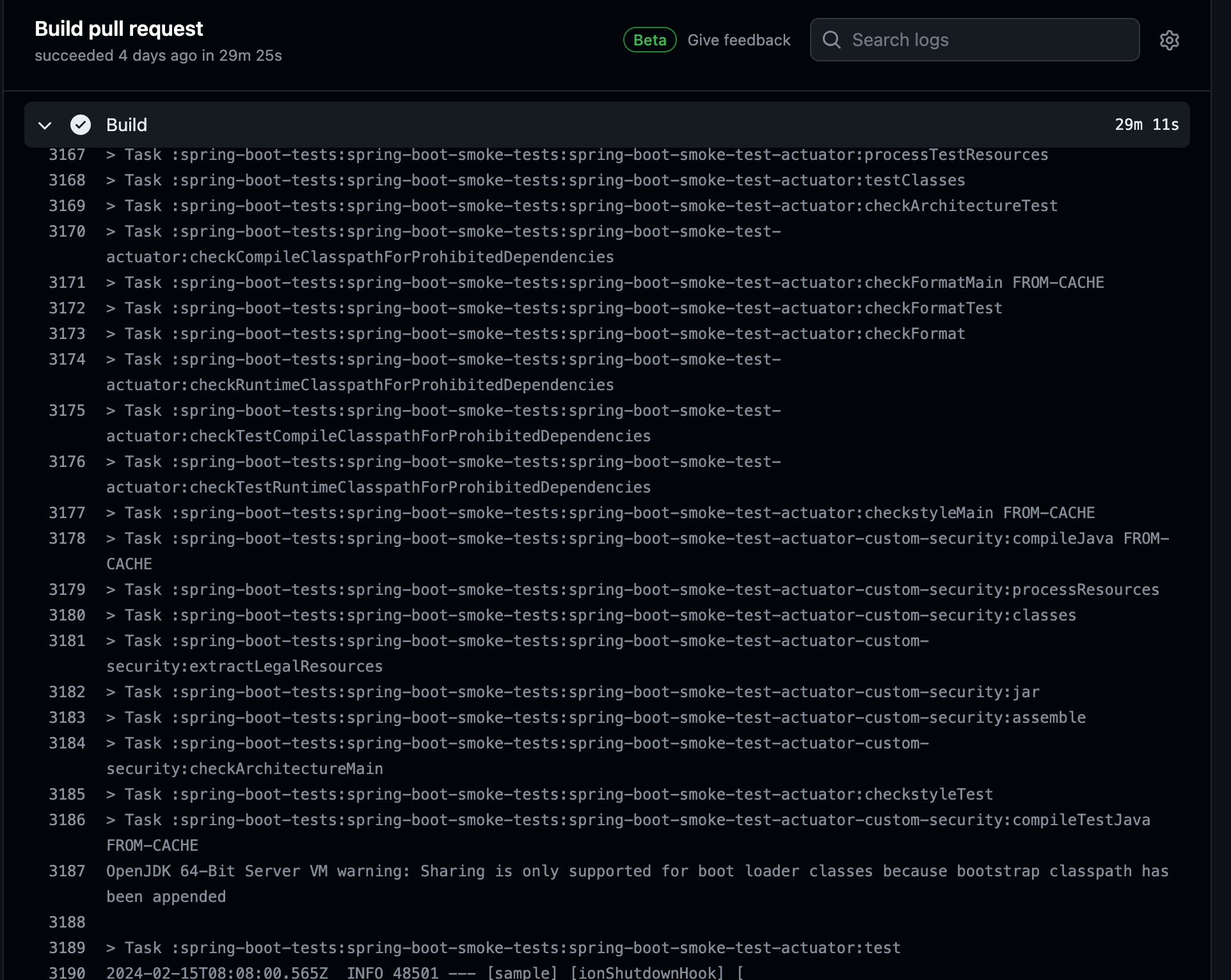
You can see it consume 29 minutes to finish the build. All the tasks in the screenshot are related to spring boot actuator smoke test.I speculate all the changes I made are tested by the task on line 3189, and the other tasks are some system-level tests.
Spring boot’s CI tool is characterized for long building time, and its complex dependencies are the main contributor. Even so, we still see that the spring boot project team is still actively performing frequent build tests. As I write this assignment, the spring boot panel shows that new builds are still in progress. I think this is one of the reasons for the success of spring boot