Testable Design and Mocking
What is testable design, and what kinds of design in java are testable?
In Java, achieving a testable design is about adhering to principles and practices that minimize coupling, maximize cohesion, and facilitate isolation of components for testing. It involves strategic use of design patterns, architectural decisions that favor testability, and leveraging tools and frameworks that support automated testing. This approach not only makes your code more testable but also improves its overall design and maintainability.
Dummy code in Spring boot
Unfortunately, finding a code that is hard to test is nearly impossible in Spring Boot.In other words, Spring Boot is a near perfect project(in testable level), which is in line with its dominant position in the java framework system.
Here is the reason why hard-to-test code hardly exists in Spring Boot:
1. Spring DI IOC container
One of the major features of spring boot is the extensive use of Java reflection for dependency injection and inversion of control. This is the core of spring framework.Dependency injection makes it easy to replace actual dependencies in a test environment, using a simplified implementation or an instance created specifically for testing purposes.
2. full application context @SpringBootTest
Spring provides a powerful test context framework that supports test configuration classes and test data management. Besides, Spring Boot provides rich testing support, including annotations and tools for unit testing and integration testing, such as @SpringBootTest, @DataJpaTest, @WebMvcTest, etc. These tools and annotations simplify the setup of test environments, allowing developers to quickly write and execute tests, whether for a specific layer (such as the web layer, service layer, or persistence layer) or for the entire application.
3. AutoConfiguration
Different from a traditional Spring framework, Spring Boot uses autoconfigure to ensures the consistency and correctness of configuration. In a test environment, this means that the same auto-configuration principles can be used to set up the test environment, reducing testing problems caused by improperly configured test environments.
4. Environment Abstractions
Spring Boot provides a variety of environment abstractions, such as configuration files and configuration classes, allowing developers to flexibly configure applications according to the running environment (development, testing, production, etc.). These abstractions also apply to the test environment, making it easy to adjust the configuration of the test environment (such as database connections, external services, etc.) and avoid hardcoding these settings.
In summary, I think it is extremely difficult for dummy code to exist in the spring boot repo; mostly it will be rejected by the pull request peer review; And it will be short-term existence even if it does appear.
Mocking
Mocking is a technique used in unit testing to simulate the behavior of real objects in a controlled way. It allows developers to isolate the unit of code they are testing by replacing its dependencies with mock objects. These mock objects can mimic the behavior of complex, real-world dependencies such as databases, web services, or other external systems without the overhead of setting up actual connections or state. Mocking is particularly useful in situations where the real dependencies are unreliable, slow, or difficult to configure for testing purposes.
Mocking is typically achieved using specialized libraries or frameworks designed for this purpose. Some popular mocking frameworks in the Java ecosystem include Mockito, JMock, and EasyMock. These frameworks provide annotations and APIs to create mock objects, define their behavior (e.g., specifying what values they should return when certain methods are called), and verify that they were interacted with in expected ways.
Spring Boot
In the process of observing spring boot testing, I found that spring boot rarely uses mocking to test their components. In spring boot philosophy, they tend to make the testing more simply. Spring Boot encourages testing with real components to ensure that parts of the application work together as expected. According to my rough statistics, only 1% of the code uses mockito, and most of this is intentional.
I made two test cases in spring boot actuator smoke test here is the detailed case:
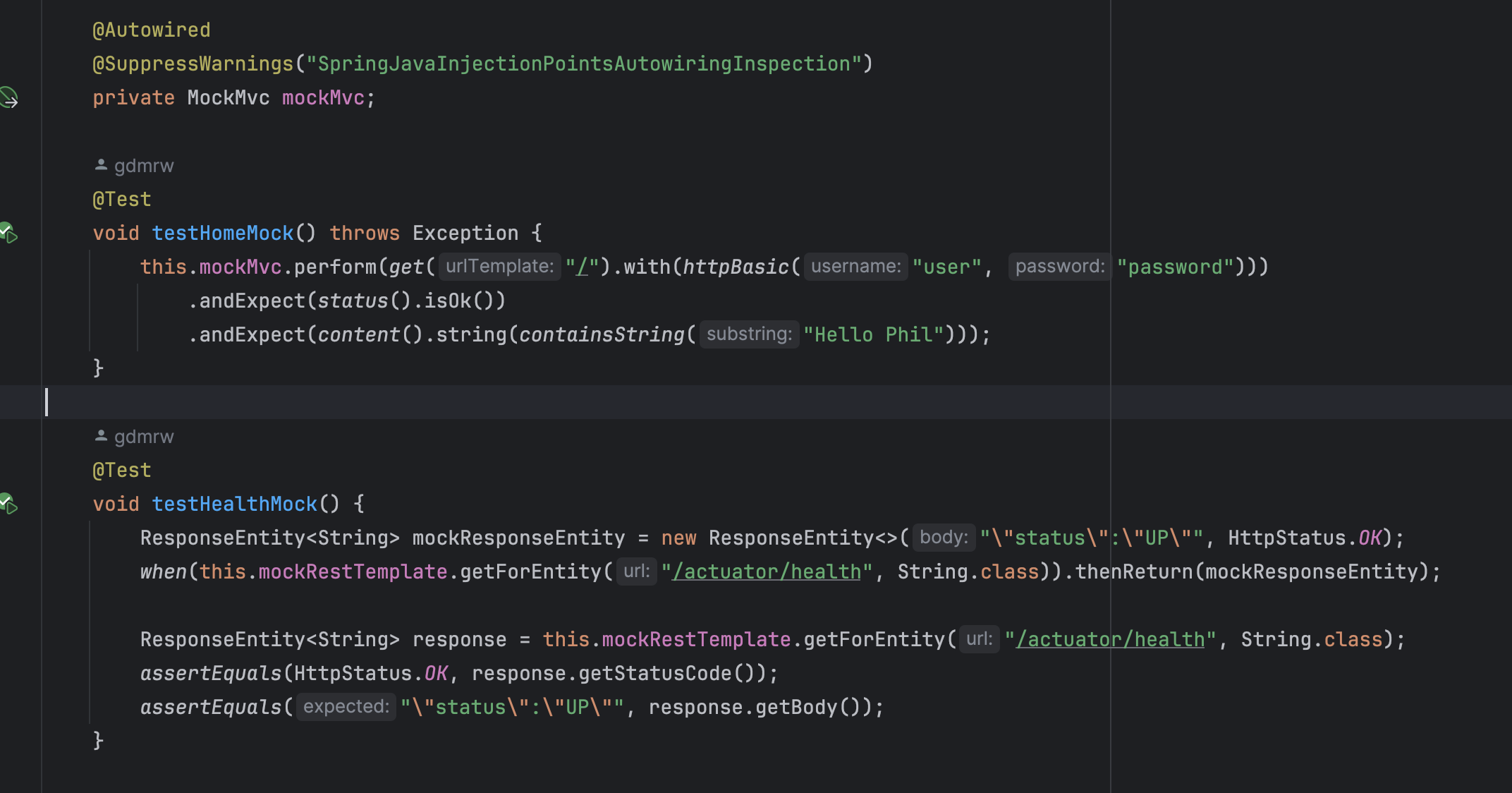
The first case use the build-in mock call mockMvc, the other one is traditional mockito.
The first one is preferred in a current scenario. The mockito one is runnable but not recommended.
MockMvc provides a powerful API that allows you to simulate HTTP requests and responses in order to test the behavior of the web layer without starting a full HTTP server. Mockito is more used for general unit testing, especially when you need to simulate class or method behavior.
The first one interacts directly with the spring boot controller, constructs an http request, and verifies the response status code
The second one created a fictional ResponseEntity and mock the RestTemplate, the MockResponseEntity will return when specific url get call. The ResponseEnitity will return a small string that is some of the expected data and a http status code. However, this method has limitations because it does not actually construct an http request and call the actuator component, and may not reflect the real situation when the system is deployed.
Both tests passed.